Blood Glucose Regulation Feedback Loop
Introduction
Claret glucose regulation involves maintaining blood glucose levels at constant levels in the face of dynamic glucose intake and energy use by the torso. Glucose, shown in figure 1 is cardinal in the free energy intake of humans. On average this target range is 60-100 mg/dL for an adult although people can be asymptomatic at much more varied levels. In order to maintain this range there are two main hormones that command blood glucose levels: insulin and glucagon. Insulin is released when in that location are loftier amounts of glucose in the blood stream.
Glucagon is released when there are low levels of glucose in the claret stream. In that location are other hormones that effect glucose regulation and are mainly controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. Blood glucose regulation is very of import to the maintenance of the human body. The brain doesn't take any energy storage of its ain and as a upshot needs a constant menses of glucose, using about 120 grams of glucose daily or near lx% of total glucose used by the body at resting state. [1] With out proper blood glucose regulation the brain and other organs could starve leading to death.
Hormones
Insulin
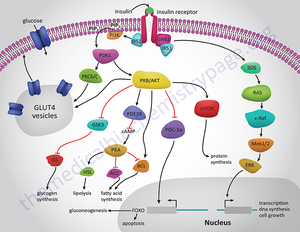
A key regulatory pathway to control blood glucose levels is the hormone insulin. Insulin is released from the beta cells in the islets of Langerhans institute in the pancreas. Insulin is released when there is a loftier concentration of glucose in the blood stream. The beta cells know to release insulin through the fallowing pathway depicted in figure two. [two,3]Glucose enters the cell and ATP is produce in the mitochondria through the Krebs bicycle and electron send chain. This increase in ATP causes channels to closes. These channels allow potassium cations to flow into the cell. [2,3,]With these channels closed the within of the cell becomes more negative causing calcium channels to open allowing calcium cations to flow into the jail cell. Calcium cation ions flow into the cell due to a concentration and elector chemic gradient that favors the influx of calcium cations. Calcium ions are key in the vesicle excretion processes. A poly peptide on the vesicle chosen the v-SNARE protein becomes entangled with a t-SNARE poly peptide on the beta prison cell surface. With calcium facilitating the interaction among the SNARE proteins the vesicle is forced to merge with the prison cell membrane and insulin is excreted into the blood stream.[2,three,four,v]
Insulin travels through the blood stream to muscle, brain or adipose tissue. In one case in that location, the insulin binds to a dimeric transmembrane receptor. This receptor autophosphorylates and causes many downstream pathways relating to glucose regulation, energy storage and Deoxyribonucleic acid transcription. For the glucose regulation pathway the receptor autophosphorylates so causes insulin receptor substrate one (IRS-i) to be phosphorated[2,3,iv]. IRS-1 and then phosphorylates Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). PI3K cleaves Phosphatidylinositol iv,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) leaving diacyl glycerol (DAG) in the cell membrane and inositol 1,iv,5-trisphosphate (IP3) in the cytosol. IP3 travels to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and cause calcium channels to open in the SER, releasing cations into the cytosol. DAG activates a kinase named protein kinase C which also opens calcium channels in the SER.[ii,three] This ambient increase in calcium facilitates the binding of vesicles to the membrane. These vesicles have Glut4 proteins imbedded in the membrane. Glut4 proteins are channel proteins that let glucose into the cell. Once these vesicles bind with the jail cell membrane glucose flows through the Glut4 protein and into the jail cell, reducing blood glucose levels.[ii,three] The process past which insulin is degraded and metabolized is poorly understood. However it is known that the liver is responsible for the bulk of insulin break down. Since the liver is so important to proper insulin levels when the liver is damaged perhaps past alcohol the regulatory organisation can be interfered with. Alcohol effects on the regulation of blood glucose will be addressed later in this article. The kidney is likewise key in the intermission downward of insulin. Peripheral tissue is thought to hold on to insulin perhaps reversibly binding to membrane receptors.[vi] These ways it is possible for insulin to be removed from the blood stream with out being broken down. Insulin clearance rates are shown to decrease in those who are obese or have diabetes. This may create insensitivity to insulin. [7]
Glucagon
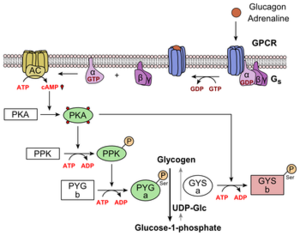
When blood glucose levels are depression, glucagon is released which inhibits the intermission down of glucose, glycolysis and activates the formation of glucose, gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis creates glucose from such molecules every bit pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids. Glucagon is released from the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.[eight] Glucose is brought into the cell through SLC2A1 channel proteins. The glucose is then used to generate ATP. This increase in ATP opens potassium channels different in beta cells where they are inhibited. This increase in intercellular potassium causes calcium channels to open up which facilitates the binding of vesicles contain glucagon. Glucagon is then released into the blood stream. This pathway is shown in figure iii Glucagon primarily operates on the liver. In one case the hormone has made it through the claret stream to the liver it binds to a transmembrane protein called a 1000 protein coupled receptor(GPCR). The associated M protein is phosphorylated with GTP and the alpha unit of the Thousand protein moves to activate adenylate cyclase (AC). AC converts ATP into cyclic AMP (campsite). [8,nine] Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase A (PKA). PKA phosphorylates phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-ii) and fructose bisphosphatase- 2(FBPase-2). Due to the addition of the phosphate PFK-2 becomes less agile. This in plough reduces the corporeality of fructose two,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP) being produce. High levels of F-2,6-BP cause glycolysis or the suspension down of glucose.[eight,9] So less active PFK-2 decreases the corporeality of F-2,6-BP. In addition FBPase-2 is activated which breaks downs F-2,6-BP which likewise decreases the amount of F-two,half dozen-BP. Depression levels of F-two,six-BP crusade the activation of FBPase-1 which increase gluconeogenesis. In addition at that place is no activation of PFK-1, which is involved in glycolysis both of these actions increase the amount of claret glucose.[9]
Epinephrine
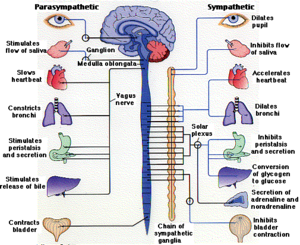
Effects of the Sympathetic Nervous System[four].
During farthermost stimuli the sympathetic nervous system kicks into activity. This is colloquially known as the fight or flight response illustrated in effigy iv. The brain sends signals throughout the body to increase heart rate, cause bronchial dilation and haptic glucose release. The brain likewise sends signals to the adrenal glands. Epinephrine is released from the adrenal glands. This hormone is fundamental to the prolonged sympathetic response. [4,ten]Epinephrine produces like results every bit the initial neuronal signal however information technology is longer lasting. Epinephrine travels through the blood stream and causes the liver to release glucose thus increasing blood glucose levels in society to exist ready for the threat. [four,ten] The pathway by which this occurs is outlined hither. Epinephrine binds to a transmembrane receptor on the liver known as the beta-adrenergic receptor protein. The receptor activates a G protein which so activates. [four,eleven]The G protein activates by swapping out at Gdp for a GTP. In one case activated the K protein diffuses along the membrane. The Grand poly peptide then binds with and activates adenylyl cyclase. Adenylyl cyclase causes ATP to become circadian AMP (cAMP).The molecule campsite binds with poly peptide kinase-A which phosporalayts specific proteins. In this footstep phosphorylase is phosphorylated.[4,xi] Phosphorylase then cuts glucogen creating a glucose-1-phosphate. This is further refined into glucose-6-phosphate by phosphoglucomutase. Glucose-6-phosphate tin then be used for energy requirements necessary in the sympathetic nervous organization response. This allows for more ATP in the muscle and encephalon.[four,xi] This hormone pathway is reversed when the parasympathetic nervous system takes priority.This organization is sometimes referred to equally the "rest and digest".[10,eleven] An experiment was conducted past Cherrington and colleagues that looked at the effects of blood glucose levels afterwards exogenic epinephrine was inserted. This experiment conducted in conscious dogs looked at hepatic glucose release and showed a fifty% increase in hepatic glucose release in response to an corporeality of epinephrine seen in a moderate stress response.[21,22]
Diabetes Mellitus
When there is a upshot with the ability of the human body to use glucose due to a trouble with the insulin pathway diabetes mellitus (diabetes mellitus) may be at mistake. At that place are a few types of diabetes mellitus with the nearly common being: type 1 diabetes mellitus, type 2 Diabetes mellitus and gestational Diabetes mellitus.[12,thirteen]
Type one Blazon 1diabetes mellitus is often discovered early in a persons' life and has besides been called juvenile diabetes mellitus. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is where no insulin is made. This is due to damage to the pancreatic beta cells, oft due to an autoimmune disorder. With out insulin the glucose tin can non go into the cells and will non brand energy. Equally a result handling for blazon 1 diabetes mellitus is regular injections of insulin. [12,13]
Blazon 2 Type diabetes mellitus is a condition where the torso becomes resistant to insulin or not enough insulin is fabricated. People who are obese have a high risk for contracting type 2 Diabetes mellitus. Although at that place is no cure for type two careful monitoring of exercise and nutrition tin can help. Other effects of the body are in increased rate of stroke and heart issues. Besides damage to minor blood vessels can occur. This happens particularly in the eyes (diabetic retinopathy) and kidneys (renalopathy). Also due to increased amounts of sugar in the blood stream a diabetic is at a college risk of infection and wounds will accept longer to heal.[12,13]
Alcohol furnishings on glucose regulation
Alcohol rapidly effects glucose levels in the blood stream which can be a challenge for those dealing with Diabetes mellitus. Alcohol effects many parts of the body and as a upshot has many pathways for effecting blood glucose levels. Alcohol can cause i to make poor decisions which will outcome how yous consume, this very directly furnishings blood glucose levels. [14,15]Booze also interacts with the hypothalamus which is responsible for, amidst other things, the drive to feed.[14] Beyond the neurological effects of alcohol on the body at that place are metabolic effects as well.This upshot is more than dramatic with drinks high in carbohydrates such a beer. The carbohydrates in beer can be metabolized and create glucose creating a temporary increment in blood glucose levels. Alcohol has energetic properties to its molecular structure and equally a result the body can gain energy from it. Through the use of enzymes: alcohol dehydrogenase, cytochrome P450, catalase alcohol is broken down. Alcohol dehydrogenase, the principal enzyme in this catabolic reaction, produces NADH.NADH is the free energy molecule that drives lactic acid formation. Glucose is turned into pyruvate through the use of ATP and so into lactic acid with NADH. This increase of NADH leads to a decrease in glucose [15]. The enzyme cytochrome P450 is activated when heavy drinking occurs. This enzyme strips an electron from NADPH in the metabolism of alcohol, which requires energy.[fifteen,xvi] This is another mechanism by which blood glucose levels would fall afterward drinking. Even so studies on the effects of alcohol go out one wanting for straight forward data on blood glucose levels in existent life situations. In an article published past Gin et al. the findings show no adverse effects on diabetic participants after moderate alcohol consumption. The American Diabetes Association and other medical information outlets concur with this finding, that moderate consumption of alcohol produce no adverse effects. However acute ingestion of alcohol has also been reported to increment insulin secretion, resulting in low blood glucose.[15,17]
Effects of Booze on Liver[5].
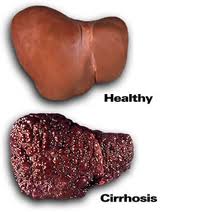
Research also indicates that heavy drinking will cause insulin to become ineffective, resulting in high blood carbohydrate levels. It is unclear if the loftier blood sugar levels are from heavy drinking alone or are continued to obesity. Further complicating this is a high correlation between heavy drinking and obesity. Also a review of the furnishings of booze indicates that both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis will be inhibited. (cederbaum,2012) As the liver is key in the release of glucose into the blood stream and issue with it can prevent good for you maintenance of blood glucose levels. With heavy drinking the liver volition become fatty reducing it's effectiveness at releasing energy stores. A disease where inflammation of the liver causes issues with the liver function is called alcoholic hepatitis. The liver can also get hard with heavy drinking due to scare tissue formation this is called fibrosis this is shown in effigy 5. The pancreas is vital for blood glucose regulation and alcohol can accept a significant effect on this organ. The pancreas creates digestive enzymes to metabolize the alcohol and these enzymes destabilize the cell membrane of the pancreatic cells. This leaves the jail cell liable to car-digestion.
Gut Bacteria
A connexion has been shown between decreased gut bacteria diversity and obesity.[eighteen] Obesity is a hazard factor for T2DM. [nineteen] However a causal relationship between gut microbiota and obesity has all the same to exist proven.[18] In addition obesity doesn't necessarily crusade one to take T2DM. In the united states 34% of adults are obese where just xi% have T2DM.[19] It is possible that a change in gut micro flora could cause diabetes simply that connection has yet to exist shown. An experiment preformed by Bäckhed and colleagues that could shed light on this showed a germ costless mice maintained forty% less body weight compared to control mice. This trend was nonetheless seen in germ gratuitous mice who received a feeding regiment and then that their caloric intake was 29% higher than conventionally raised mice. When these mice received gut microbiota their body fat increase 57% and became "dramatically insulin resistant".[xviii,20]
Conclusion
All cells in the man body require glucose to survive. Even so excessive amounts of glucose can also exist detrimental to the body. In social club to maintain this residue the trunk uses hormonal regulation. The body will detect loftier levels of blood glucose and release insulin to allow the sugar into cells. If there is not enough claret glucose, glucagon will be released. This hormone will cause the formation of glucose and the release of glucose stores. If the trunk is presented with a threat information technology will initiate the sympathetic nervous system. Part of this response is the release of epinephrine which causes haptic glucose release. If the torso tin not properly regulate blood glucose levels than it may be a form of diabetes. Diabetes type i stems from an inability to produce insulin. Diabetes blazon two is due to an insensitivity to insulin. Due to the blood glucose regulatory systems broad reach on the torso when alcohol which as well has a whole torso effect a reaction is bond to occur. Claret glucose levels may initially increase withal this is merely in the case of high carbohydrate alcoholic beverages, such equally beer. Due to the metabolism of booze glucose will be turned into pyruvate and blood glucose levels volition drop. Booze's effects on judgment are also likely to lead to a driblet in blood sugar.
References
[one] Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer 50. Biochemistry. 5th edition. New York: Westward H Freeman; 2002. Section 30.2, Each Organ Has a Unique Metabolic Profile. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22436/
[2] Chang, L., Chiang, S.-H., & Saltiel, A. R. (2004). Insulin Signaling and the Regulation of Glucose Ship. Molecular Medicine, 10(7-12), 65–71. http://doi.org/10.2119/2005-00029.Saltiel
[3][ndsuvirtualcell] (Dec 3, 2009) Insulin Signaling (Point Pathways)(YouTube) Retrieved from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FkkK5lTmBYQ Gin H1, Morlat P, Ragnaud JM, Aubertin J. (1992) Brusk-term effect of red vino (consumed during meals) on insulin requirement and glucose tolerance in diabetic patients. Retrieved from:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1499475
[iv][Moof University] (Dec 3, 2013) Insulin Signaling Cascade - Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (YouTube )Retrieved from: https://world wide web.youtube.com/lookout man?v=2YR1XmYF5hM
[5]Albertsr. (n.d) Essential Cell Biology: Fourth Edition. New York: Garland Science.
[6] WILLIAM C. DUCKWORTH and ABBAS E. KITABCHI(1981) Insulin Metabolism and Degradation Endocrine Reviews ii:2, 210-233 Kovacs B, Stoppler M (2014) Booze and diet Retrieved from:http://www.medicinenet.com/alcohol_and_nutrition/page4.htm
[7] William C. Duckworth, Robert G. Bennett, and Frederick G. Hamel (1998) Insulin Degradation: Progress and Potential Endocrine Reviews 19:5, 608-624
[8]Quesada, I., Tuduri, E., Ripoll, C., & Nadal, A. (2008). Physiology of the pancreatic -cell and glucagon secretion: Function in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Journal of Endocrinology, 5-19.
[9] [Moof University] (Dec three, 2013) Glucagon Signaling Cascade - GPCR (Grand-Poly peptide Coupled Receptor) (YouTube)Retrieved from:https://www.youtube.com/lookout?v=1ImdVTWKiqs9
[10] Bear, Grand(due north.d) Neuroscience: Exploring the Encephalon. New York: Wolter Kluwer
[11] Krantz,B Principles of Metabolic Regulation, Illustrated with Glucose and Glycogen Metabolism [pdf] Retrieved from:https://mcb.berkeley.edu/labs/krantz/mcb102/lect_S2008/MCB102-SPRING2008-LECTURE7-METABOLIC_REGULATION.pdf
[12] American Diabetes Association. (due north.d.). Retrieved December 12, 2015, from http://world wide web.diabetes.org
[13]Dansinger, M. (Ed.). (2014, September 2). Controlling Diabetes: When Pills Are Not Plenty, With Pictures. Retrieved Dec 12, 2015, from http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/controlling-diabetes-14/slideshow-control-your-blood-sugars
[xiv]Yeomans, One thousand. (northward.d.). Short term effects of alcohol on appetite in humans. Effects of context and restrained eating. Appetite, 565-573.
[15] HAMS: Impairment reduction for alcohol (How Alcohol Is Metabolized in the Man Body) http://world wide web.hamsnetwork.org/metabolism/
[16]Caton, S., Brawl, Yard., Ahern, A., & Hetherington, M. (n.d.). Dose-dependent furnishings of booze on appetite and food intake. Physiology & Behavior, 51-58.
[17]Cederbaum, A. I. (2012). ALCOHOL METABOLISM. Clinics in Liver Disease, 16(iv), 667–685. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2012.08.002
[18] Musso, G.(2010). Obesity, Diabetes, and Gut Microbiota The hygiene hypothesis expanded?, vol. 33 no. ten 2277-2284.doi: 10.2337/dc10-0556
[19]Eckel, R. (2011). Obesity and Blazon 2 Diabetes: What Can Exist Unified and What Needs to Be Individualized?vol. 34 no. 6 1424-1430.doi: x.2337/dc11-0447
[20] Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI: The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004;101:15718–15723
[21] Cherrington Ad, Diamond MP, Light-green DR, Williams PE: Prove for an intra- hepatic contribution to the waning effect of glucagon on glucose product in the conscious dog. Diabetes 31:917–922, 1982
[22] Cherrington Advertising,(1997) Control of Glucose Uptake and Release past the Liver In Vivo [pdf]. Retrieved from: http://rodrigoborges.hospedagemdesites.ws/principal/pdf/endocrino_07.pdf
Blood Glucose Regulation Feedback Loop,
Source: https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Blood_Glucose_Regulation
Posted by: zaratenowbod.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Blood Glucose Regulation Feedback Loop"
Post a Comment